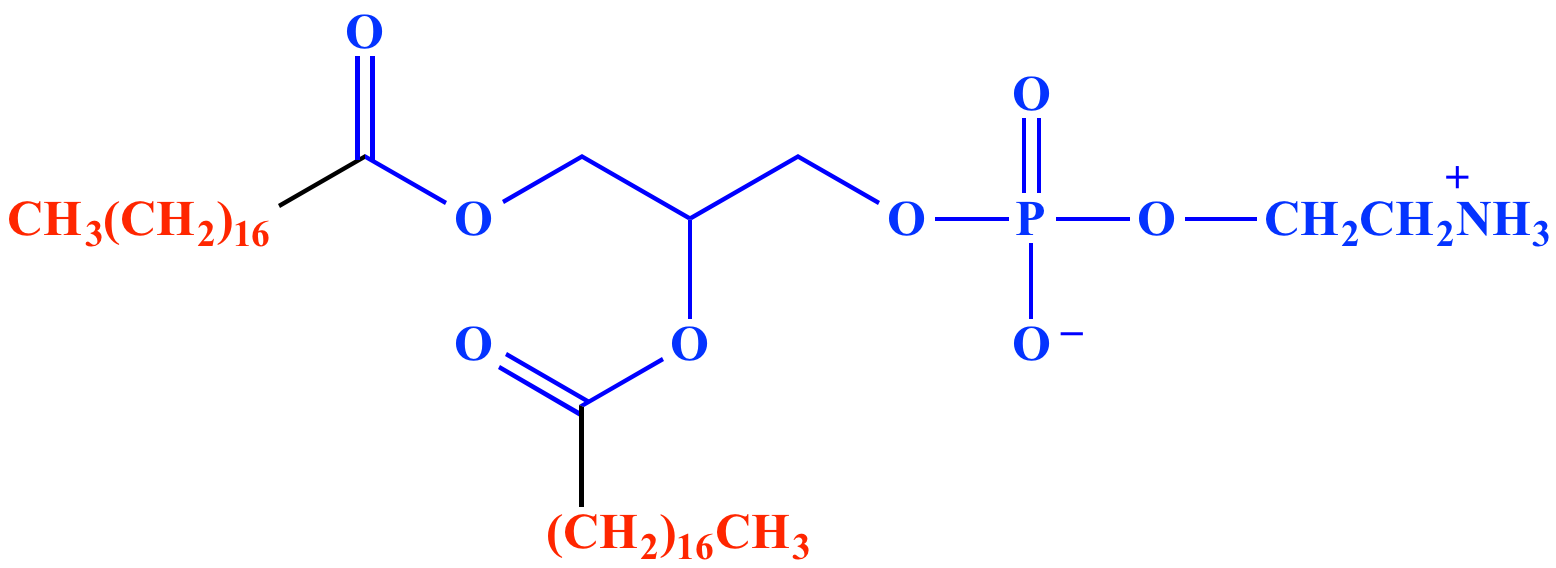
Fatty Acids Are Amphiphilic In Nature Because . such molecules are termed amphiphilic (gk. these primitive meteorites are enriched in organic compounds, including amino acids and a variety of amphiphilic molecules; The common feature of these lipids is that they are all esters of moderate to long chain fatty acids. amphipathic or amphiphilic molecules have parts that are polar and nonpolar, making them both hydrophilic and lipophilic. Fatty acids made up of ten or more carbon atoms are nearly. differences in the length and saturation of the fatty acid tails are important because they influence the ability of phospholipid molecules to pack against one another,. phospholipids are a special type of lipid associated with cell membranes and typically have a glycerol (or sphingosine) backbone to. in the bilayer interior, the hydrophobic tails (that is, the fatty acid portions of lipid molecules) interact by means of london's forces. Amphi = both) or amphipathic.
from www.chem.ucla.edu
these primitive meteorites are enriched in organic compounds, including amino acids and a variety of amphiphilic molecules; Fatty acids made up of ten or more carbon atoms are nearly. differences in the length and saturation of the fatty acid tails are important because they influence the ability of phospholipid molecules to pack against one another,. phospholipids are a special type of lipid associated with cell membranes and typically have a glycerol (or sphingosine) backbone to. in the bilayer interior, the hydrophobic tails (that is, the fatty acid portions of lipid molecules) interact by means of london's forces. Amphi = both) or amphipathic. The common feature of these lipids is that they are all esters of moderate to long chain fatty acids. such molecules are termed amphiphilic (gk. amphipathic or amphiphilic molecules have parts that are polar and nonpolar, making them both hydrophilic and lipophilic.
Illustrated Glossary of Organic Chemistry Amphiphilic
Fatty Acids Are Amphiphilic In Nature Because these primitive meteorites are enriched in organic compounds, including amino acids and a variety of amphiphilic molecules; phospholipids are a special type of lipid associated with cell membranes and typically have a glycerol (or sphingosine) backbone to. such molecules are termed amphiphilic (gk. differences in the length and saturation of the fatty acid tails are important because they influence the ability of phospholipid molecules to pack against one another,. in the bilayer interior, the hydrophobic tails (that is, the fatty acid portions of lipid molecules) interact by means of london's forces. The common feature of these lipids is that they are all esters of moderate to long chain fatty acids. amphipathic or amphiphilic molecules have parts that are polar and nonpolar, making them both hydrophilic and lipophilic. Amphi = both) or amphipathic. these primitive meteorites are enriched in organic compounds, including amino acids and a variety of amphiphilic molecules; Fatty acids made up of ten or more carbon atoms are nearly.
From dxouhoqlj.blob.core.windows.net
Fatty Acids Are Considered Amphiphilic Because at Kevin Travis blog Fatty Acids Are Amphiphilic In Nature Because such molecules are termed amphiphilic (gk. differences in the length and saturation of the fatty acid tails are important because they influence the ability of phospholipid molecules to pack against one another,. amphipathic or amphiphilic molecules have parts that are polar and nonpolar, making them both hydrophilic and lipophilic. in the bilayer interior, the hydrophobic tails. Fatty Acids Are Amphiphilic In Nature Because.
From courses.lumenlearning.com
Lipids Microbiology Fatty Acids Are Amphiphilic In Nature Because Amphi = both) or amphipathic. these primitive meteorites are enriched in organic compounds, including amino acids and a variety of amphiphilic molecules; Fatty acids made up of ten or more carbon atoms are nearly. phospholipids are a special type of lipid associated with cell membranes and typically have a glycerol (or sphingosine) backbone to. such molecules are. Fatty Acids Are Amphiphilic In Nature Because.
From courses.lumenlearning.com
Components and Structure OpenStax Biology 2e Fatty Acids Are Amphiphilic In Nature Because Amphi = both) or amphipathic. The common feature of these lipids is that they are all esters of moderate to long chain fatty acids. Fatty acids made up of ten or more carbon atoms are nearly. amphipathic or amphiphilic molecules have parts that are polar and nonpolar, making them both hydrophilic and lipophilic. phospholipids are a special type. Fatty Acids Are Amphiphilic In Nature Because.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Chapter 2 Aqueous Chemistry PowerPoint Presentation, free Fatty Acids Are Amphiphilic In Nature Because amphipathic or amphiphilic molecules have parts that are polar and nonpolar, making them both hydrophilic and lipophilic. Amphi = both) or amphipathic. these primitive meteorites are enriched in organic compounds, including amino acids and a variety of amphiphilic molecules; The common feature of these lipids is that they are all esters of moderate to long chain fatty acids.. Fatty Acids Are Amphiphilic In Nature Because.
From thebiologynotes.com
Shouri Kushal, Author at The Biology Notes Fatty Acids Are Amphiphilic In Nature Because amphipathic or amphiphilic molecules have parts that are polar and nonpolar, making them both hydrophilic and lipophilic. such molecules are termed amphiphilic (gk. Amphi = both) or amphipathic. Fatty acids made up of ten or more carbon atoms are nearly. The common feature of these lipids is that they are all esters of moderate to long chain fatty. Fatty Acids Are Amphiphilic In Nature Because.
From www.researchgate.net
Fatty acid biosynthesis pathway in the palm tree. DGAT1, diacylglycerol Fatty Acids Are Amphiphilic In Nature Because Fatty acids made up of ten or more carbon atoms are nearly. Amphi = both) or amphipathic. such molecules are termed amphiphilic (gk. differences in the length and saturation of the fatty acid tails are important because they influence the ability of phospholipid molecules to pack against one another,. in the bilayer interior, the hydrophobic tails (that. Fatty Acids Are Amphiphilic In Nature Because.
From www.researchgate.net
Amphiphilic nature of DNA, cellulose and surfactants. Download Fatty Acids Are Amphiphilic In Nature Because Fatty acids made up of ten or more carbon atoms are nearly. Amphi = both) or amphipathic. phospholipids are a special type of lipid associated with cell membranes and typically have a glycerol (or sphingosine) backbone to. differences in the length and saturation of the fatty acid tails are important because they influence the ability of phospholipid molecules. Fatty Acids Are Amphiphilic In Nature Because.
From dxouhoqlj.blob.core.windows.net
Fatty Acids Are Considered Amphiphilic Because at Kevin Travis blog Fatty Acids Are Amphiphilic In Nature Because these primitive meteorites are enriched in organic compounds, including amino acids and a variety of amphiphilic molecules; in the bilayer interior, the hydrophobic tails (that is, the fatty acid portions of lipid molecules) interact by means of london's forces. Amphi = both) or amphipathic. The common feature of these lipids is that they are all esters of moderate. Fatty Acids Are Amphiphilic In Nature Because.
From www.lecturio.com
Fatty Acids and Lipids Concise Medical Knowledge Fatty Acids Are Amphiphilic In Nature Because phospholipids are a special type of lipid associated with cell membranes and typically have a glycerol (or sphingosine) backbone to. in the bilayer interior, the hydrophobic tails (that is, the fatty acid portions of lipid molecules) interact by means of london's forces. differences in the length and saturation of the fatty acid tails are important because they. Fatty Acids Are Amphiphilic In Nature Because.
From www.researchgate.net
Fatty acid biosynthesis and categories of fatty acidderived natural Fatty Acids Are Amphiphilic In Nature Because differences in the length and saturation of the fatty acid tails are important because they influence the ability of phospholipid molecules to pack against one another,. Amphi = both) or amphipathic. The common feature of these lipids is that they are all esters of moderate to long chain fatty acids. Fatty acids made up of ten or more carbon. Fatty Acids Are Amphiphilic In Nature Because.
From www.savemyexams.com
Triglycerides & Ester Bonds Edexcel International AS Biology Revision Fatty Acids Are Amphiphilic In Nature Because Fatty acids made up of ten or more carbon atoms are nearly. such molecules are termed amphiphilic (gk. phospholipids are a special type of lipid associated with cell membranes and typically have a glycerol (or sphingosine) backbone to. amphipathic or amphiphilic molecules have parts that are polar and nonpolar, making them both hydrophilic and lipophilic. The common. Fatty Acids Are Amphiphilic In Nature Because.
From slideplayer.com
Lipids of Physiological Significance ppt download Fatty Acids Are Amphiphilic In Nature Because amphipathic or amphiphilic molecules have parts that are polar and nonpolar, making them both hydrophilic and lipophilic. The common feature of these lipids is that they are all esters of moderate to long chain fatty acids. differences in the length and saturation of the fatty acid tails are important because they influence the ability of phospholipid molecules to. Fatty Acids Are Amphiphilic In Nature Because.
From www.numerade.com
SOLVEDGlycerophospholipids are amphiphilic molecules that contain two Fatty Acids Are Amphiphilic In Nature Because differences in the length and saturation of the fatty acid tails are important because they influence the ability of phospholipid molecules to pack against one another,. The common feature of these lipids is that they are all esters of moderate to long chain fatty acids. Fatty acids made up of ten or more carbon atoms are nearly. such. Fatty Acids Are Amphiphilic In Nature Because.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Biosynthesis of Fatty Acids LIPOGENESIS PowerPoint Presentation Fatty Acids Are Amphiphilic In Nature Because differences in the length and saturation of the fatty acid tails are important because they influence the ability of phospholipid molecules to pack against one another,. The common feature of these lipids is that they are all esters of moderate to long chain fatty acids. Amphi = both) or amphipathic. in the bilayer interior, the hydrophobic tails (that. Fatty Acids Are Amphiphilic In Nature Because.
From www.youtube.com
Amphipathic Molecules Biochemistry YouTube Fatty Acids Are Amphiphilic In Nature Because in the bilayer interior, the hydrophobic tails (that is, the fatty acid portions of lipid molecules) interact by means of london's forces. differences in the length and saturation of the fatty acid tails are important because they influence the ability of phospholipid molecules to pack against one another,. Amphi = both) or amphipathic. The common feature of these. Fatty Acids Are Amphiphilic In Nature Because.
From www.albert.io
Lipids AP® Biology Crash Course Review Albert.io Fatty Acids Are Amphiphilic In Nature Because in the bilayer interior, the hydrophobic tails (that is, the fatty acid portions of lipid molecules) interact by means of london's forces. these primitive meteorites are enriched in organic compounds, including amino acids and a variety of amphiphilic molecules; such molecules are termed amphiphilic (gk. amphipathic or amphiphilic molecules have parts that are polar and nonpolar,. Fatty Acids Are Amphiphilic In Nature Because.
From www.youtube.com
10 Amphipathic Lipids Lipid Chemistry10 Biochemistry N'JOY Fatty Acids Are Amphiphilic In Nature Because amphipathic or amphiphilic molecules have parts that are polar and nonpolar, making them both hydrophilic and lipophilic. phospholipids are a special type of lipid associated with cell membranes and typically have a glycerol (or sphingosine) backbone to. in the bilayer interior, the hydrophobic tails (that is, the fatty acid portions of lipid molecules) interact by means of. Fatty Acids Are Amphiphilic In Nature Because.
From justlife.noknow.info
Types of fatty acids and their functions Justlife Fatty Acids Are Amphiphilic In Nature Because phospholipids are a special type of lipid associated with cell membranes and typically have a glycerol (or sphingosine) backbone to. these primitive meteorites are enriched in organic compounds, including amino acids and a variety of amphiphilic molecules; differences in the length and saturation of the fatty acid tails are important because they influence the ability of phospholipid. Fatty Acids Are Amphiphilic In Nature Because.